| How are sand dunes formed? | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › how deserts are formed ielts › How are sand dunes formed? |
How are sand dunes formed?
|
How are sand dunes formed?
The conditions required for sand dune formation are: a large supply of sand a large flat beach time for the sand to dry, so an extensive tidal range is needed an onshore wind (wind blowing from the sea to the land) for sand to be transported to the back of the beach an obstacle for the dune to form against, e.g. pebble or driftwoodThe image below shows Harlech beach, North Wales. Its sizeable tidal range supports the development of sand dunes. The tidal range is the difference between the high tide and the following low tide.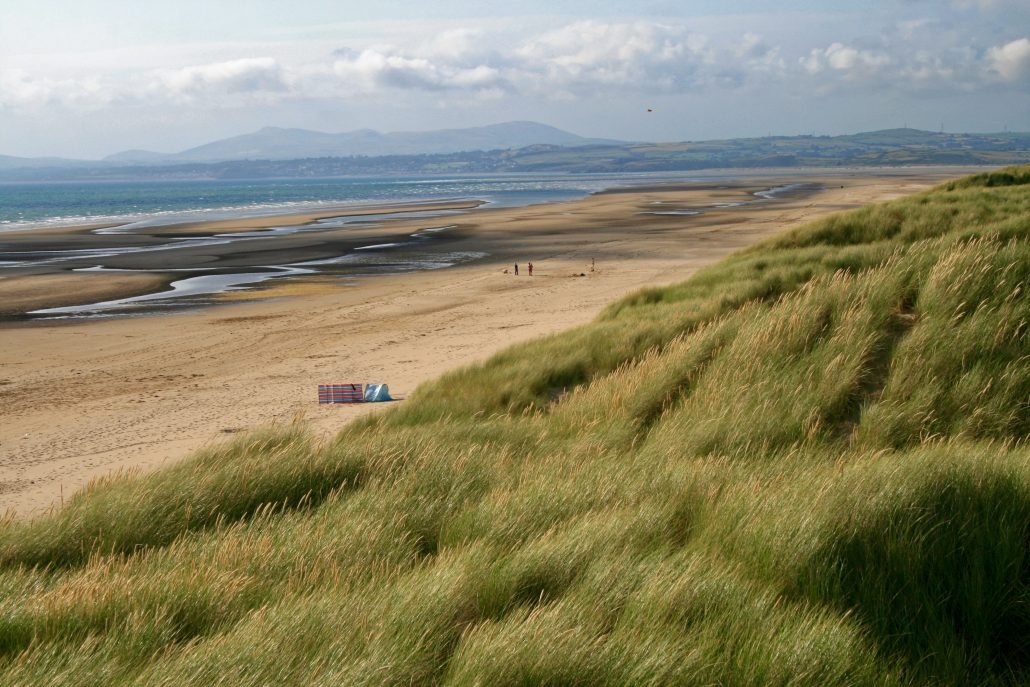  A beach with a large tidal range How does wind transport sand?Aeolian Transport is the first process of coastal dune formation and involves the movement and weathering of sand particles behind and along the shoreline. Aeolian transportation is when the wind transports sediment. Wind transports sand in 3 ways. These are: suspension saltation creep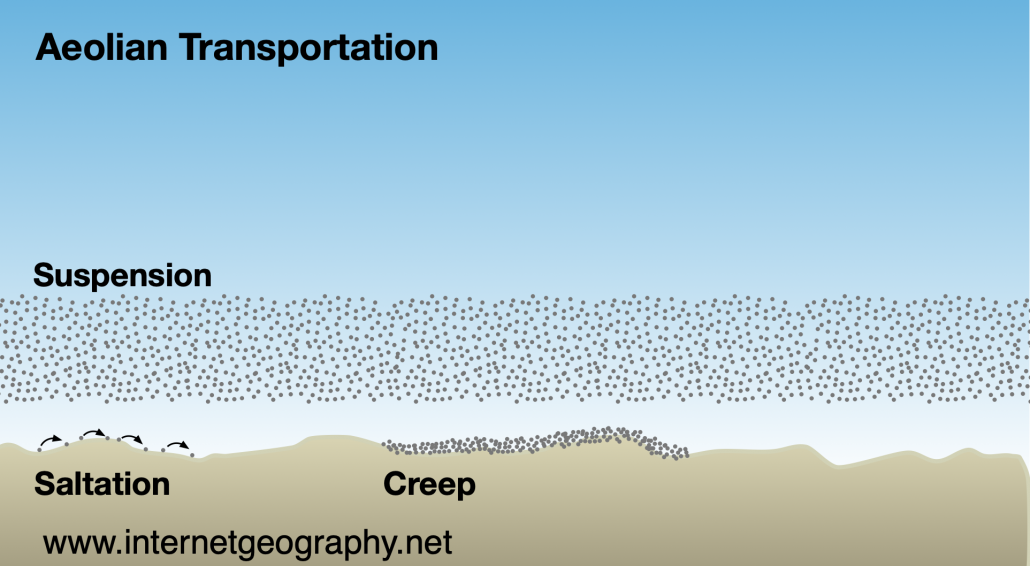 Aeolian transportation 1% of the movement of sand is by suspension when sand is picked up and carried within the wind. 95% of sand movement results from saltation when grains of sand bounce along the beach as they are picked up and dropped by the wind. Finally, 4% of transportation is by creep when sand grains collide and push each other along. The video below shows a combination of these processes of transportation. As the wind blows up the beach, it will transport material. Larger pieces of sediment will rest against an obstacle forming a ridge, while smaller particles will settle on the other side. On the side facing the wind, the material begins to reach a crest. This is because the pile of material becomes steep and unstable and begins to collapse. When this happens, smaller particles fall down the other side. Once there is a stable angle (30-34 degrees), the sand stops slipping, and the cycle repeats. As the sand becomes an obstacle, more dunes may form in front of it— the stronger the wind, the higher the dunes. The characteristics of sand dunes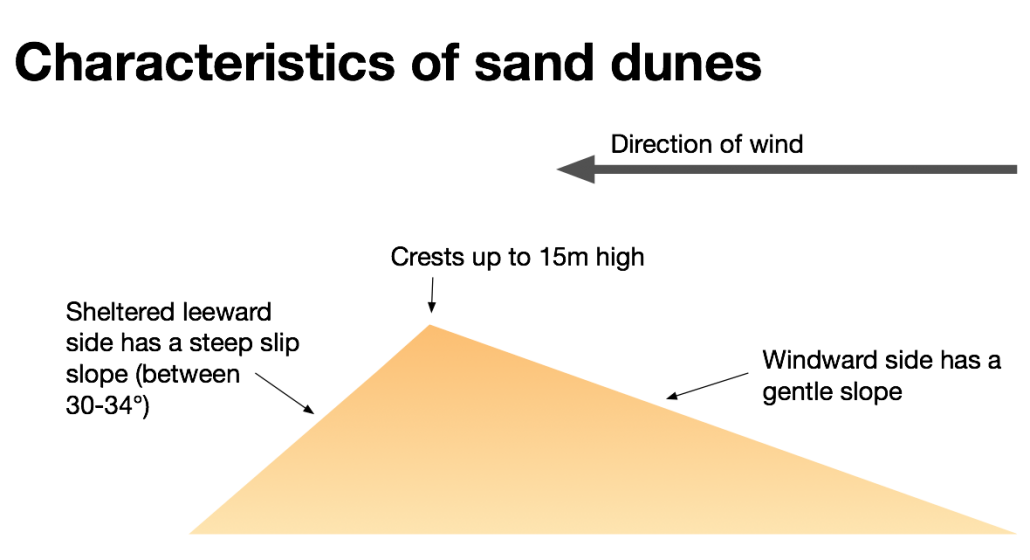 Characteristics of sand dunes Sand dunes have: a gentle slope on the side the wind blows against a steep side on the sheltered side (30-34 degrees) a crest (top of the sand dune) up to 15 metres How do sand dunes change as you move inland? How do sand dunes change with distance from the beach? Dunes become taller further inland. Embryo dunes (youngest sand dunes) are only a few metres high whereas mature dunes are up to 15m high. This is because marram grass and other vegetation colonise the sand dune and hold it together with long roots, stopping the migration of the dune. Dunes closer to the beach are more yellow, whereas further away, they are grey due to humous and bacteria from plants and animals being added. A trough separates each dune (dip), called a slack. They are formed by the removal of sediment from the sheltered lee side of the dune and the windward side of the next dune. Slacks can be eroded so much that they reach the water table resulting in the formation of salty dunes. The video below illustrates how vegetation in a dune ecosystem changes as you move inland (vegetation succession). The 360° aerial image below shows the sand dunes at Morfaa Harlech nature reserve in North Wales. The image below shows vegetation succession on dunes at Harlech, North Wales.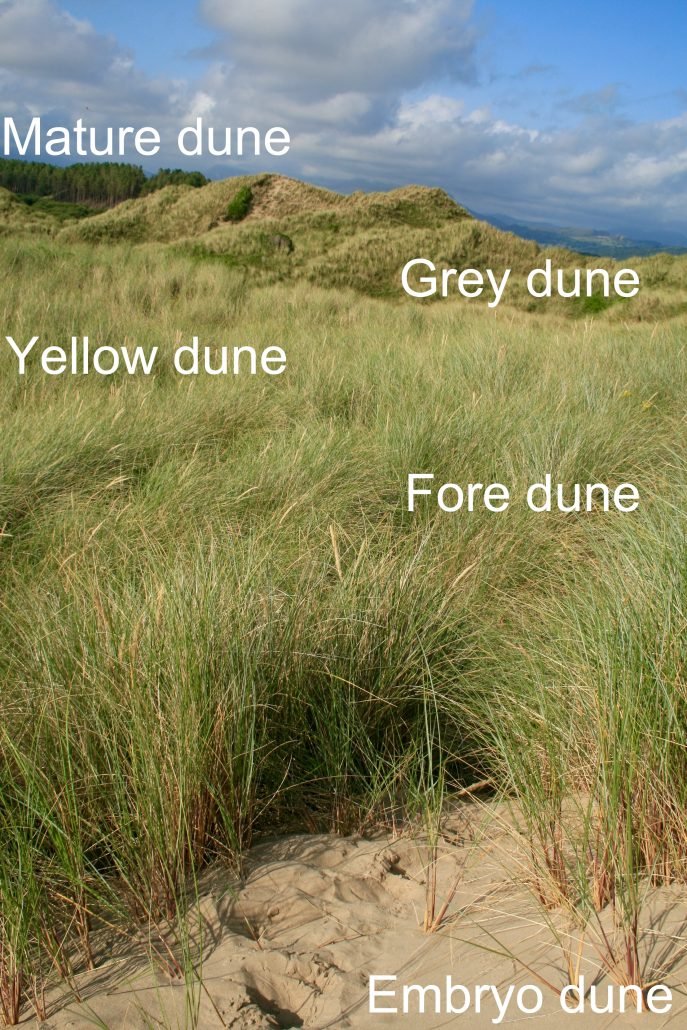  Sand dune vegetation succession The video below shows the extent of roots and illustrates how vegetation helps stabilise dunes. |
【本文地址】